publications
2025
- ICML
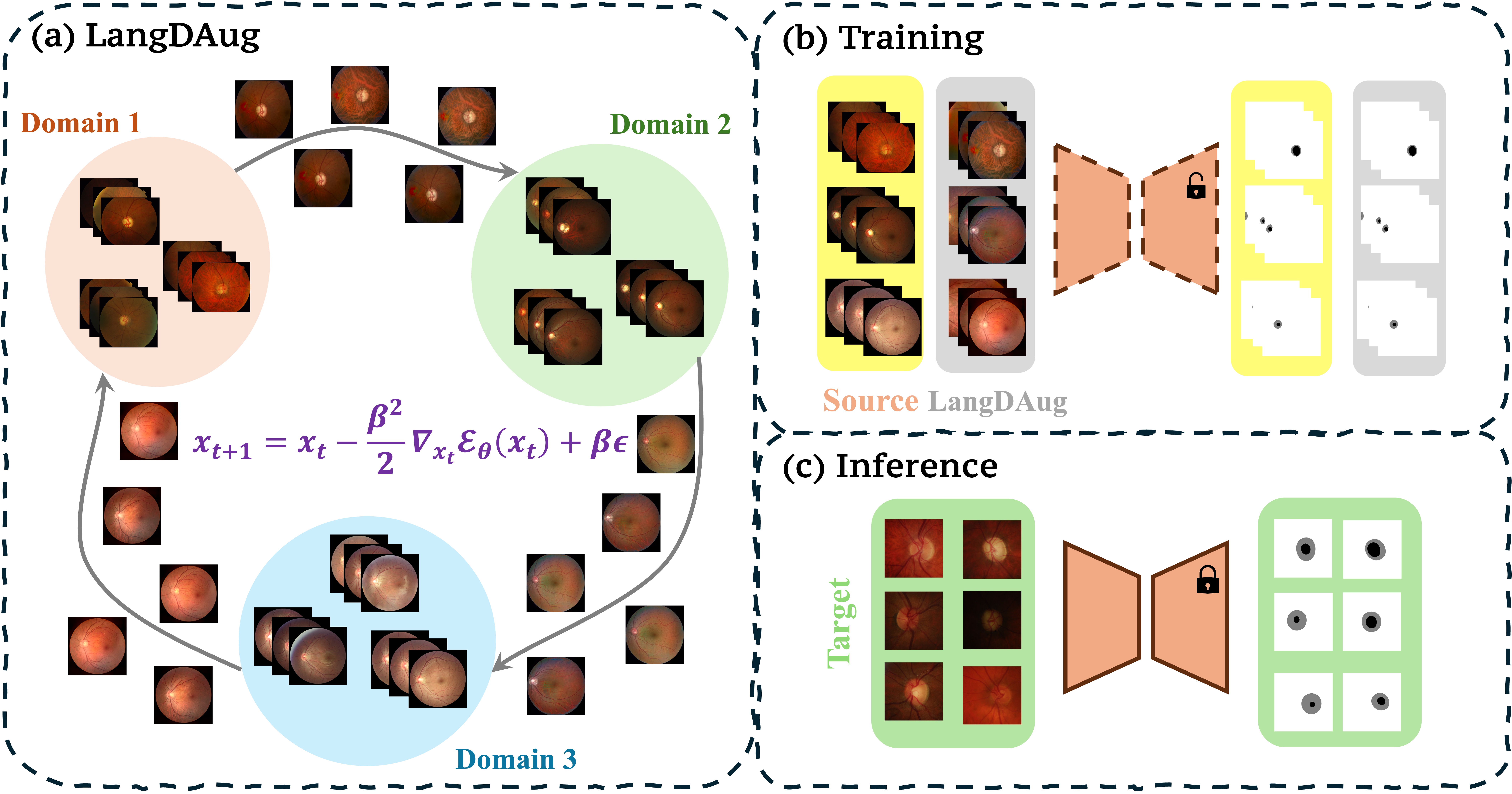 LangDAug: Langevin Data Augmentation for Multi-Source Domain Generalization in Medical Image SegmentationPiyush Tiwary, Kinjawl Bhattacharyya, and Prathosh APIn International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025
LangDAug: Langevin Data Augmentation for Multi-Source Domain Generalization in Medical Image SegmentationPiyush Tiwary, Kinjawl Bhattacharyya, and Prathosh APIn International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2025Medical image segmentation models often struggle to generalize across different domains due to various reasons. Domain Generalization (DG) methods overcome this either through representation learning or data augmentation (DA). While representation learning methods seek domain-invariant features, they often rely on ad-hoc techniques and lack formal guarantees. DA methods, which enrich model representations through synthetic samples, have shown comparable or superior performance to representation learning approaches. We propose LangDAug, a novel Langevin Data Augmentation for multi-source domain generalization in 2D medical image segmentation. LangDAug leverages Energy-Based Models (EBMs) trained via contrastive divergence to traverse between source domains, generating intermediate samples through Langevin dynamics. Theoretical analysis shows that LangDAug induces a regularization effect, and for GLMs, it upper-bounds the Rademacher complexity by the intrinsic dimensionality of the data manifold. Through extensive experiments on Fundus segmentation and 2D MRI prostate segmentation benchmarks, we show that LangDAug outperforms state-of-the-art domain generalization methods and effectively complements existing domain-randomization approaches.
@inproceedings{tiwary2024langdaug, title = {LangDAug: Langevin Data Augmentation for Multi-Source Domain Generalization in Medical Image Segmentation}, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Bhattacharyya, Kinjawl and AP, Prathosh}, booktitle = {International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML)}, year = {2025}, url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=LB5F02kwAv}, } - TMLR
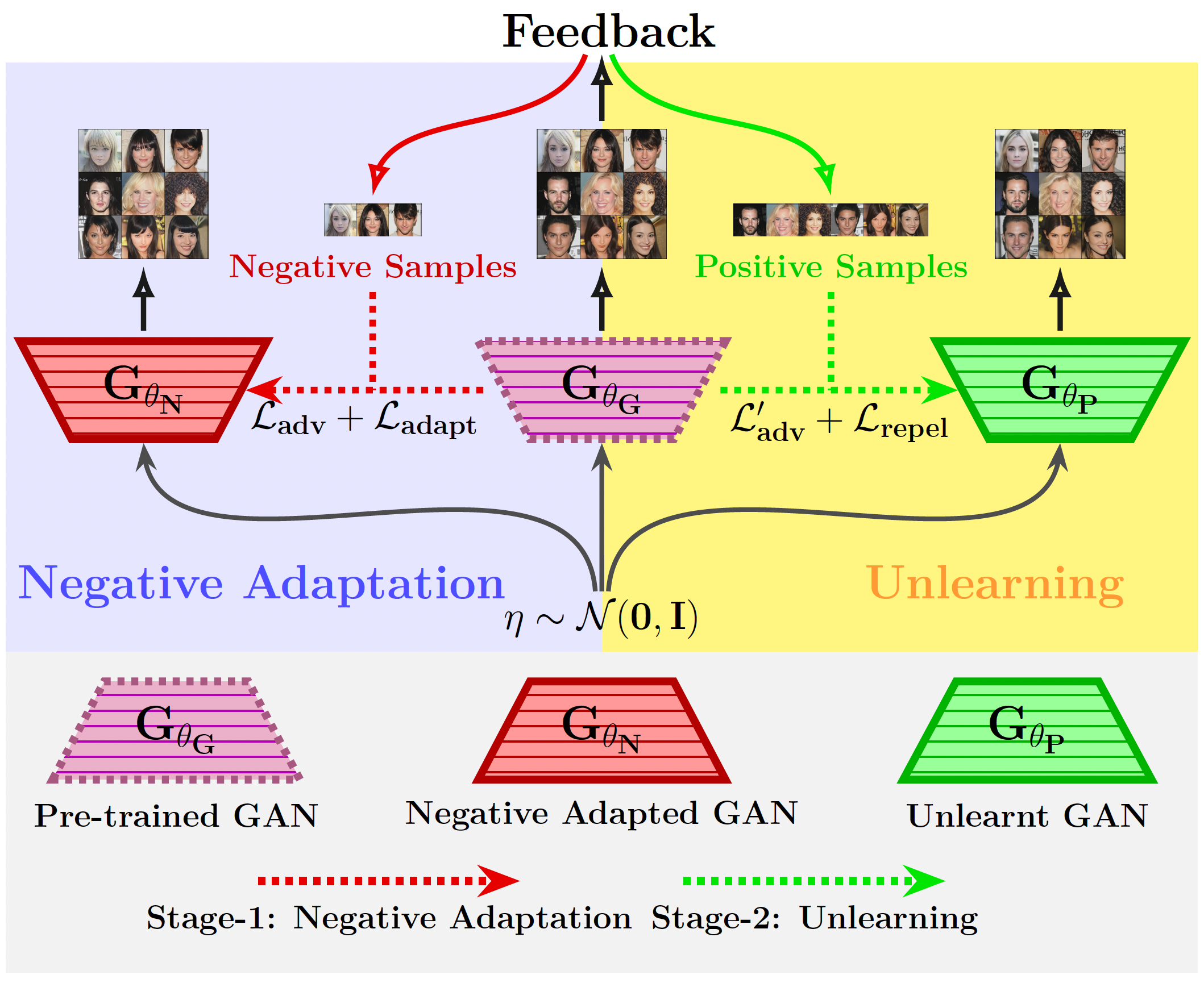 Adapt then Unlearn: Exploring Parameter Space Semantics for Unlearning in Generative Adversarial NetworksPiyush Tiwary, Atri Guha, Subhodip Panda, and 1 more authorTransactions on Machine Learning Research, 2025
Adapt then Unlearn: Exploring Parameter Space Semantics for Unlearning in Generative Adversarial NetworksPiyush Tiwary, Atri Guha, Subhodip Panda, and 1 more authorTransactions on Machine Learning Research, 2025Owing to the growing concerns about privacy and regulatory compliance, it is desirable to regulate the output of generative models. To that end, the objective of this work is to prevent the generation of outputs containing undesired features from a pre-trained Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) where the underlying training data set is inaccessible. Our approach is inspired by the observation that the parameter space of GANs exhibits meaningful directions that can be leveraged to suppress specific undesired features. However, such directions usually result in the degradation of the quality of generated samples. Our proposed two-stage method, known as ’Adapt-then-Unlearn,’ excels at unlearning such undesirable features while also maintaining the quality of generated samples. In the initial stage, we adapt a pre-trained GAN on a set of negative samples (containing undesired features) provided by the user. Subsequently, we train the original pre-trained GAN using positive samples, along with a repulsion regularizer. This regularizer encourages the learned model parameters to move away from the parameters of the adapted model (first stage) while not degrading the generation quality. We provide theoretical insights into the proposed method. To the best of our knowledge, our approach stands as the first method addressing unlearning within the realm of high-fidelity GANs (such as StyleGAN). We validate the effectiveness of our method through comprehensive experiments, encompassing both class-level unlearning on the MNIST and AFHQ dataset and feature-level unlearning tasks on the CelebA-HQ dataset. Our code and implementation is available at: https://github.com/atriguha/Adapt_Unlearn.
@article{tiwary2025adapt, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Guha, Atri and Panda, Subhodip and AP, Prathosh}, journal = {Transactions on Machine Learning Research}, title = {Adapt then Unlearn: Exploring Parameter Space Semantics for Unlearning in Generative Adversarial Networks}, year = {2025}, keywords = {GANs, Unlearning}, url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=jAHEBivObO&t=1739258832039}, }
2024
- IEEE SPL
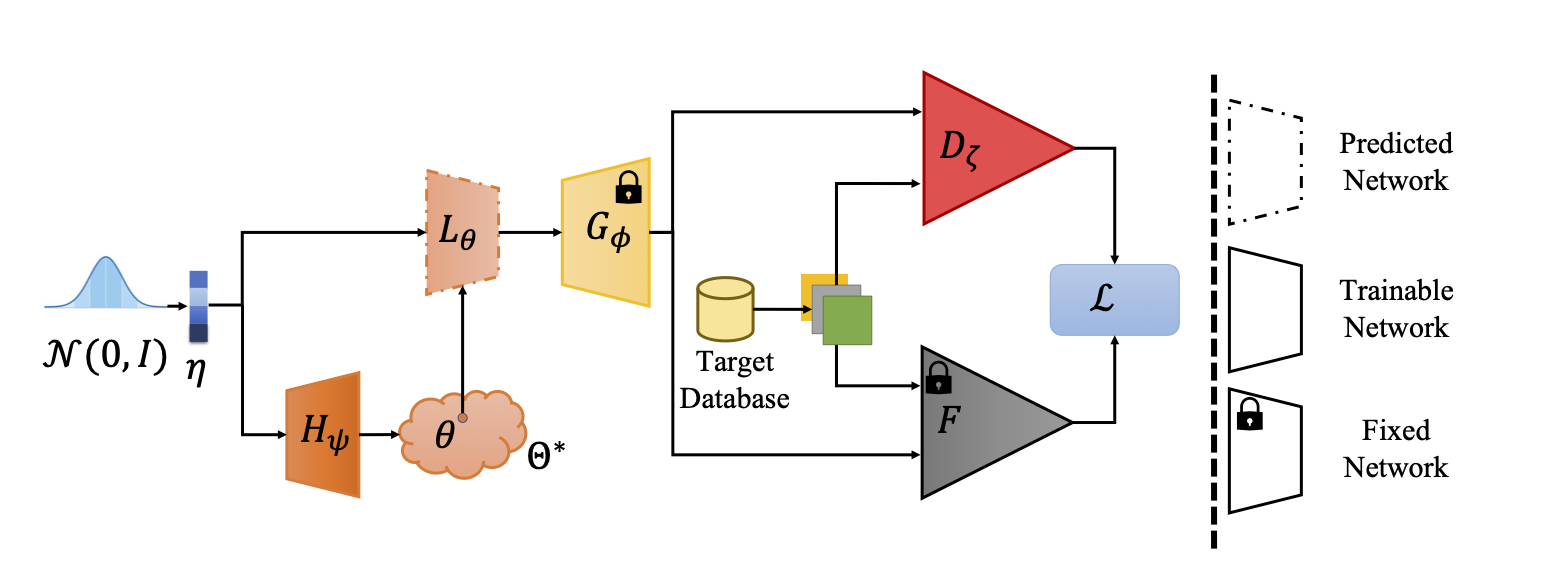 SoLAD: Sampling over Latent Adapter for Few Shot GenerationArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024
SoLAD: Sampling over Latent Adapter for Few Shot GenerationArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2024Few-shot adaptation of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) under distributional shift is generally achieved via regularized retraining or latent space adaptation. While the former methods offer fast inference, the latter generate diverse images. This work aims to solve these issues and achieve the best of both regimes in a principled manner via Bayesian reformulation of the GAN objective. We highlight a hidden expectation term over GAN parameters, that is often overlooked but is critical in few-shot settings. This observation helps us justify prepending a latent adapter network (LAN) before a pre-trained GAN and propose a sampling procedure over the parameters of LAN (called SoLAD) to compute the usually-ignored hidden expectation. SoLAD enables fast generation of quality samples from multiple few-shot target domains using a GAN pre-trained on a single source domain.
@article{10750383, author = {Mondal, Arnab Kumar and Tiwary, Piyush and Singla, Parag and AP, Prathosh}, journal = {IEEE Signal Processing Letters}, title = {SoLAD: Sampling over Latent Adapter for Few Shot Generation}, year = {2024}, keywords = {GANs, Few-shot adaptation}, doi = {10.1109/LSP.2024.3496822}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10750383}, } - IEEE WCL
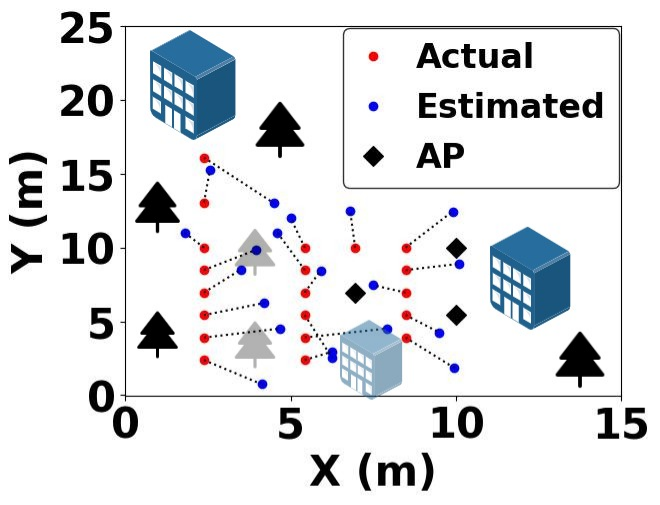 A Lightweight α- μ Fading Environment based Localization towards Edge ImplementationGaurav Prasad, Piyush Tiwary, Ankur Pandey, and 1 more authorIEEE Wireless Communication Letters, 2024
A Lightweight α- μ Fading Environment based Localization towards Edge ImplementationGaurav Prasad, Piyush Tiwary, Ankur Pandey, and 1 more authorIEEE Wireless Communication Letters, 2024This letter presents a lightweight localization method utilizing Received Signal Strength (RSS) of Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) signals considering a generic α- μ fading environment. Despite the usefulness of RSS-based methods, inaccuracies arise from signal randomness caused by shadowing and small-scale fading effects. Furthermore, fingerprinting methods are computationally exhaustive due to the multiple RSS sample collection. We consider a lightweight range-based approach, modeling small-scale fading as α\mhμdistribution, and present the formulation of a Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) estimator for deriving location estimates using a single RSS sample. Moreover, to address the issue of exploding gradients resulting from divergent terms, a clipped gradient ascent variant is proposed. The proposed estimator outperforms other estimators based on established Rayleigh, and Nakagami-m fading distributions in comprehensive tests conducted in indoor and outdoor environments. A major advantage of the proposed method is its lower computational complexity over existing methods, and hence it can be easily deployed on edge devices.
@article{10623871, author = {Prasad, Gaurav and Tiwary, Piyush and Pandey, Ankur and Kumar, Sudhir}, journal = {IEEE Wireless Communication Letters}, title = {A Lightweight ${\alpha {-} \mu}$ Fading Environment based Localization towards Edge Implementation}, year = {2024}, keywords = {Generalized fading, Localization}, doi = {10.1109/LWC.2024.3439564}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10623871}, } - UAI
 Bayesian Pseudo-Coresets via Contrastive DivergencePiyush Tiwary, Kumar Shubham, Vivek Kashyap, and 1 more authorIn Conference on Uncertainity in Artificial Intelligence (UAI), 2024
Bayesian Pseudo-Coresets via Contrastive DivergencePiyush Tiwary, Kumar Shubham, Vivek Kashyap, and 1 more authorIn Conference on Uncertainity in Artificial Intelligence (UAI), 2024Bayesian methods provide an elegant framework for estimating parameter posteriors and quantification of uncertainty associated with probabilistic models. However, they often suffer from slow inference times. To address this challenge, Bayesian Pseudo-Coresets (BPC) have emerged as a promising solution. BPC methods aim to create a small synthetic dataset, known as pseudo-coresets, that approximates the posterior inference achieved with the original dataset. This approximation is achieved by optimizing a divergence measure between the true posterior and the pseudo-coreset posterior. Various divergence measures have been proposed for constructing pseudo-coresets, with forward Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence being the most successful. However, using forward KL divergence necessitates sampling from the pseudo-coreset posterior, often accomplished through approximate Gaussian variational distributions. Alternatively, one could employ Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods for sampling, but this becomes challenging in high-dimensional parameter spaces due to slow mixing. In this study, we introduce a novel approach for constructing pseudo-coresets by utilizing contrastive divergence. Importantly, optimizing contrastive divergence eliminates the need for approximations in the pseudo-coreset construction process. Furthermore, it enables the use of finite-step MCMC methods, alleviating the requirement for extensive mixing to reach a stationary distribution. To validate our method’s effectiveness, we conduct extensive experiments on multiple datasets, demonstrating its superiority over existing BPC techniques.
@inproceedings{tiwary2024bayesian, title = {Bayesian Pseudo-Coresets via Contrastive Divergence}, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Shubham, Kumar and Kashyap, Vivek and AP, Prathosh}, booktitle = {Conference on Uncertainity in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)}, year = {2024}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.11278}, }
2023
- IEEE TNSE
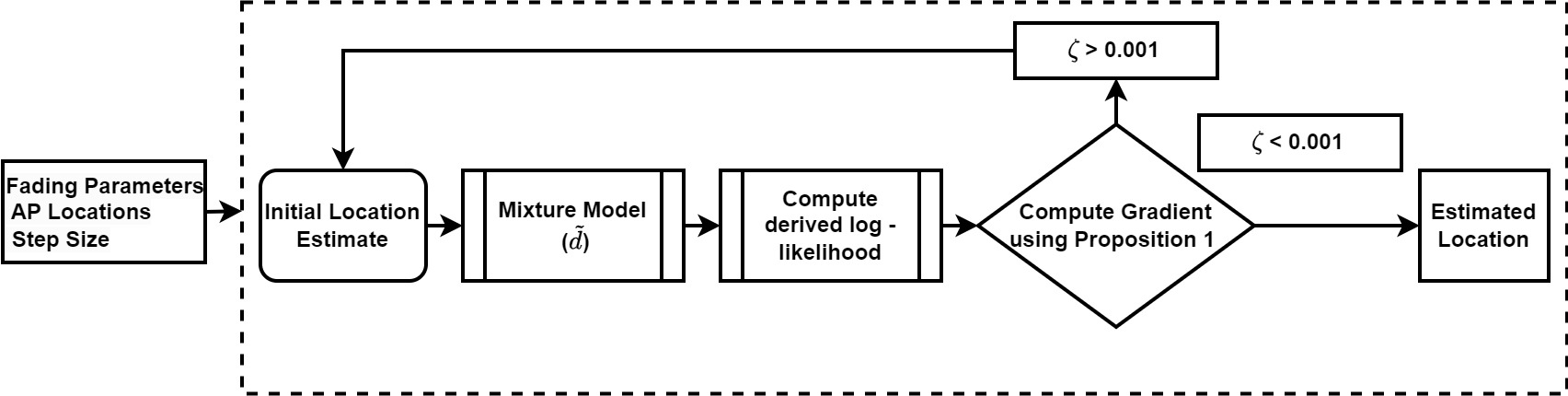 Bessel Function Mixture Model for Localization in Generalized η- μ IoT Fading EnvironmentAnkur Pandey, Piyush Tiwary, and Sudhir KumarIEEE Transactions on Network Sciences and Engineering, 2023
Bessel Function Mixture Model for Localization in Generalized η- μ IoT Fading EnvironmentAnkur Pandey, Piyush Tiwary, and Sudhir KumarIEEE Transactions on Network Sciences and Engineering, 2023The effectiveness of localization techniques that rely on Received Signal Strength (RSS) is impeded by the existence of small-scale fading and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) phenomena. Therefore, it is crucial to accurately model the fading distribution when estimating the location of smart devices. The utilisation of a generic fading model confers a significant advantage owing to its capacity to accommodate a variety of fading distributions across diverse environments. This work introduces a new approach for device localization in a connected Internet of Things (IoT) setting, utilising a generic η-μ fading model for RSS. We propose a Bessel Function mixture model that is utilised to estimate the position of the device, taking into account a generic η-μ fading model. A log-Sigmoid weight function is employed to combine large and small approximations for the modified Bessel function of the first kind. The position coordinates are estimated through a gradient ascent that seeks to optimise the derived maximum likelihood (ML) function. The method under consideration is evaluated in three distinct settings, namely an authentic indoor environment, a simulated η-μ fading environment, and an outdoor testbed. Our findings demonstrate the effectiveness of the generic fading models, surpassing current state-of-the-art methodologies.
@article{10356779, author = {Pandey, Ankur and Tiwary, Piyush and Kumar, Sudhir}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Network Sciences and Engineering}, title = {Bessel Function Mixture Model for Localization in Generalized ${\eta {-} \mu}$ IoT Fading Environment}, year = {2023}, keywords = {Generalized fading, Localization, Modified Bessel Function}, doi = {10.1109/TNSE.2023.3342622}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10356779}, } - MICCAI-MedIA
 Cycle Consistent Twin Energy-based Models for Image-to-Image TranslationPiyush Tiwary, Kinjawl Bhattacharyya, and Prathosh APMedical Image Analysis (MedIA), 2023
Cycle Consistent Twin Energy-based Models for Image-to-Image TranslationPiyush Tiwary, Kinjawl Bhattacharyya, and Prathosh APMedical Image Analysis (MedIA), 2023Domain shift refers to change of distributional characteristics between the training (source) and the testing (target) datasets of a learning task, leading to performance drop. For tasks involving medical images, domain shift may be caused because of several factors such as change in underlying imaging modalities, measuring devices and staining mechanisms. Recent approaches address this issue via generative models based on the principles of adversarial learning albeit they suffer from issues such as difficulty in training and lack of diversity. Motivated by the aforementioned observations, we adapt an alternative class of deep generative models called the Energy-Based Models (EBMs) for the task of unpaired image-to-image translation of medical images. Specifically, we propose a novel method called the Cycle Consistent Twin EBMs (CCT-EBM) which employs a pair of EBMs in the latent space of an Auto-Encoder trained on the source data. While one of the EBMs translates the source to the target domain the other does vice-versa along with a novel consistency loss, ensuring translation symmetry and coupling between the domains. We theoretically analyze the proposed method and show that our design leads to better translation between the domains with reduced langevin mixing steps. We demonstrate the efficacy of our method through detailed quantitative and qualitative experiments on image segmentation tasks on three different datasets vis-a-vis state-of-the-art methods.
@article{TIWARY2024103031, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Bhattacharyya, Kinjawl and AP, Prathosh}, journal = {Medical Image Analysis (MedIA)}, title = {Cycle Consistent Twin Energy-based Models for Image-to-Image Translation}, year = {2023}, volume = {91}, keywords = {Energy based models, Image translation, Medical image segmentation}, doi = {https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2023.103031}, url = {https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1361841523002918}, } - ICLR
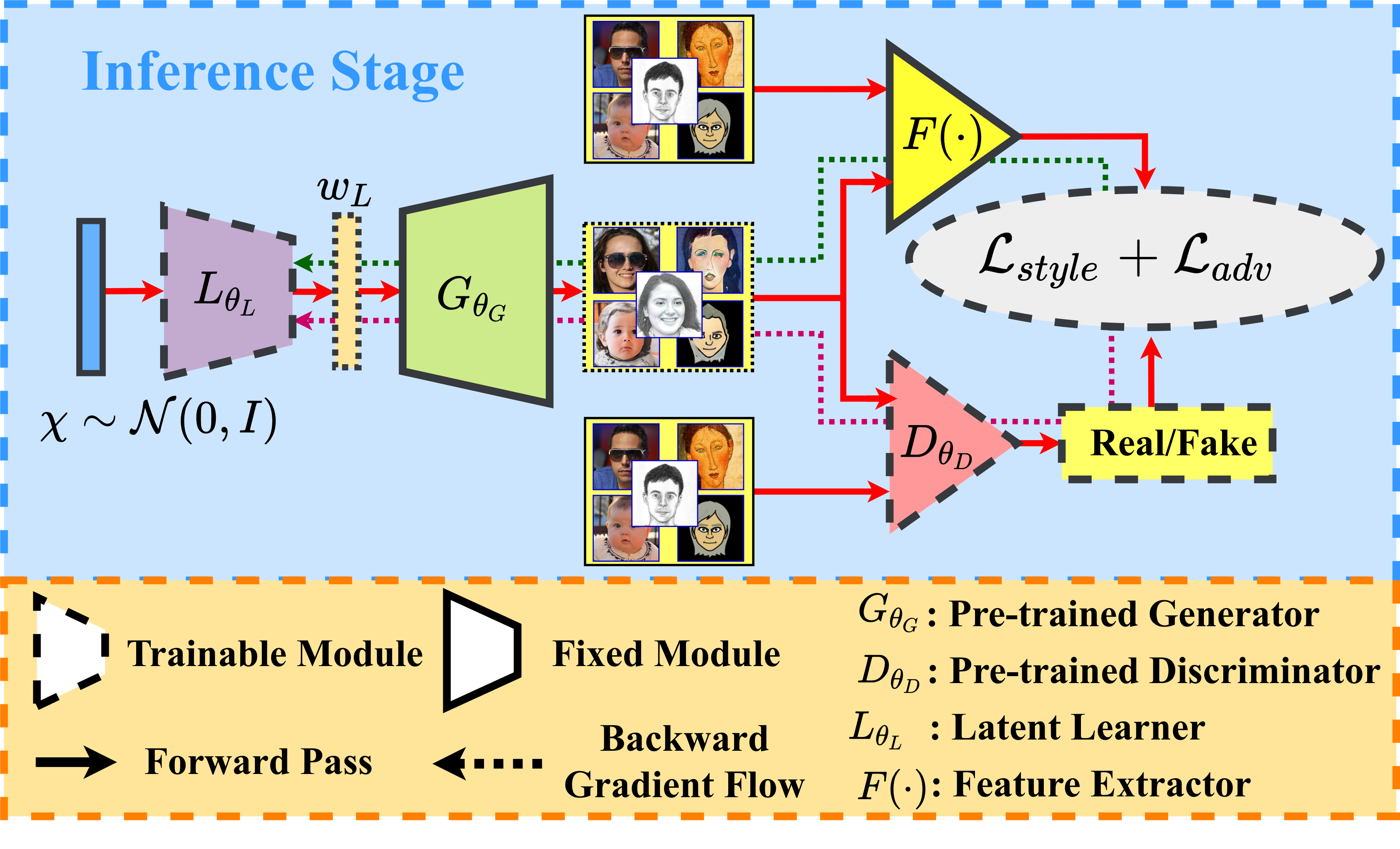 Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANsArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIn International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), 2023
Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANsArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIn International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR), 2023In this work, our objective is to adapt a Deep generative model trained on a large-scale source dataset to multiple target domains with scarce data. Specifically, we focus on adapting a pre-trained Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) to a target domain without re-training the generator. Our method draws the motivation from the fact that out-of-distribution samples can be ‘embedded’ onto the latent space of a pre-trained source-GAN. We propose to train a small latent-generation network during the inference stage, each time a batch of target samples is to be generated. These target latent codes are fed to the source-generator to obtain novel target samples. Despite using the same small set of target samples and the source generator, multiple independent training episodes of the latent-generation network results in the diversity of the generated target samples. Our method, albeit simple, can be used to generate data from multiple target distributions using a generator trained on a single source distribution. We demonstrate the efficacy of our surprisingly simple method in generating multiple target datasets with only a single source generator and a few target samples.
@inproceedings{mondal2023fewshoticlr, title = {Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANs}, author = {Mondal, Arnab Kumar and Tiwary, Piyush and Singla, Parag and AP, Prathosh}, booktitle = {International Conference on Learning Representation (ICLR)}, year = {2023}, url = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=sCYXJr3QJM8}, } - AISTATS
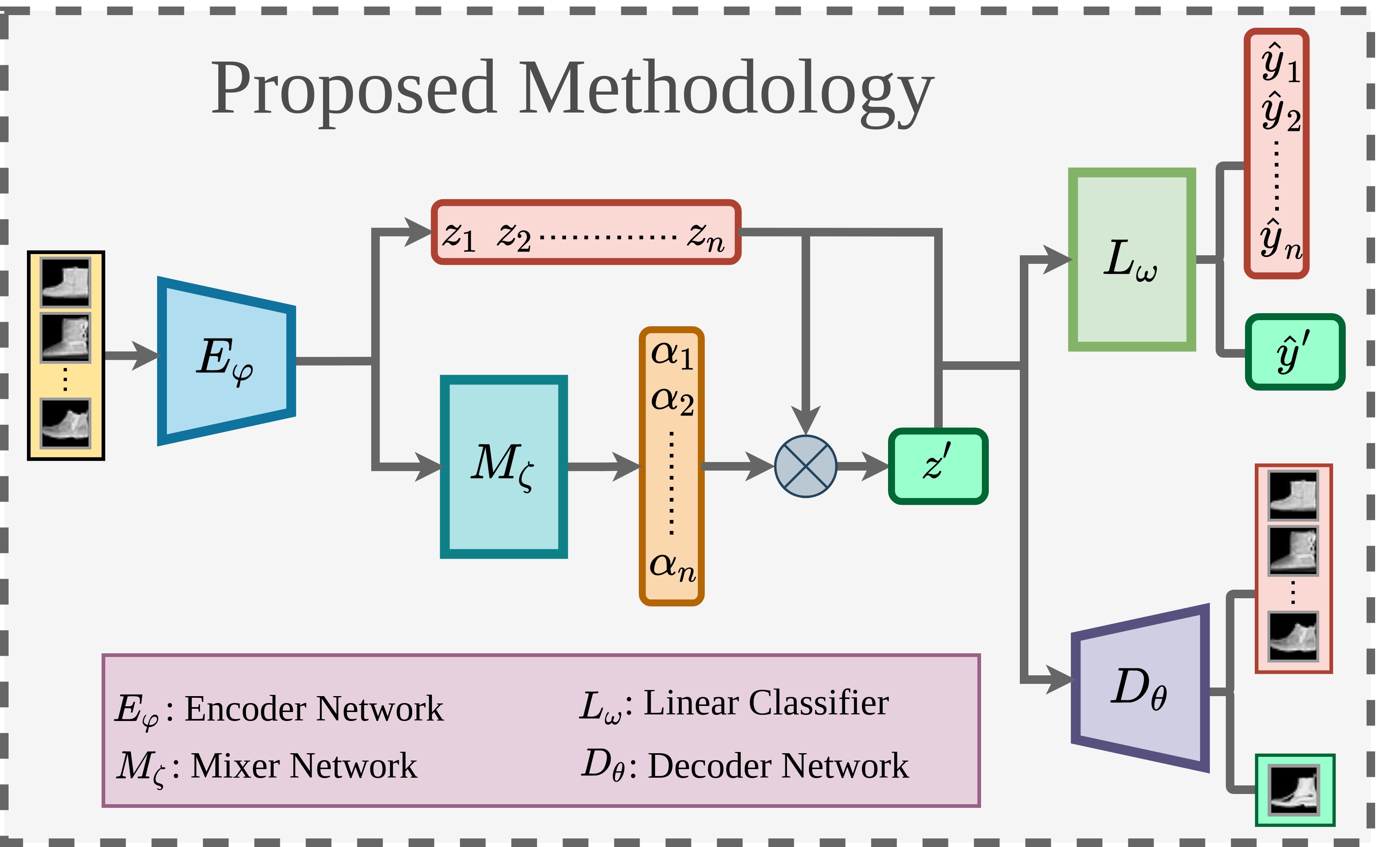 Minority Oversampling for Imbalanced Data via Class-Preserving Regularized Auto-EncodersArnab Kumar Mondal, Lakshya Singhal, Piyush Tiwary, and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), 2023
Minority Oversampling for Imbalanced Data via Class-Preserving Regularized Auto-EncodersArnab Kumar Mondal, Lakshya Singhal, Piyush Tiwary, and 2 more authorsIn International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS), 2023Class imbalance is a common phenomenon in multiple application domains such as healthcare, where the sample occurrence of one or few class categories is more prevalent in the dataset than the rest. This work addresses the class-imbalance issue by proposing an over-sampling method for the minority classes in the latent space of a Regularized Auto-Encoder (RAE). Specifically, we construct a latent space by maximizing the conditional data likelihood using an Encoder-Decoder structure, such that oversampling through convex combinations of latent samples preserves the class identity. A jointly-trained linear classifier that separates convexly coupled latent vectors from different classes is used to impose this property on the AE’s latent space. Further, the aforesaid linear classifier is used for final classification without retraining. We theoretically show that our method can achieve a low variance risk estimate compared to naive oversampling methods and is robust to overfitting. We conduct several experiments on benchmark datasets and show that our method outperforms the existing oversampling techniques for handling class imbalance.
@inproceedings{mondal2023OSA, title = {Minority Oversampling for Imbalanced Data via Class-Preserving Regularized Auto-Encoders}, author = {Mondal, Arnab Kumar and Singhal, Lakshya and Tiwary, Piyush and Singla, Parag and Prathosh, AP}, booktitle = {International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS)}, year = {2023}, url = {https://proceedings.mlr.press/v206/mondal23a.pdf}, }
2022
- NIPS Workshop
 Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANsArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIn NeurIPS 2022 Workshop on Distribution Shifts: Connecting Methods and Applications, 2022
Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANsArnab Kumar Mondal, Piyush Tiwary, Parag Singla, and 1 more authorIn NeurIPS 2022 Workshop on Distribution Shifts: Connecting Methods and Applications, 2022In this study, we adapt generative models trained on large source datasets to scarce target domains. We adapt a pre-trained Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) without retraining the generator, avoiding catastrophic forgetting and over-fitting. Starting from the observation that target images can be ’embedded’ onto the latent space of a pre-trained source-GAN, our method finds the latent code corresponding to the target domain on the source latent manifold. Optimizing a latent learner network during inference generates a novel target embedding that is supplied to the source-GAN generator to generate target samples. Our method, albeit simple, can be used to generate data from multiple target distributions using a generator trained on a single source distribution.
@inproceedings{mondal2022few, title = {Few Shot Generative Domain Adaptation Via Inference-Stage Latent Learning in GANs}, author = {Mondal, Arnab Kumar and Tiwary, Piyush and Singla, Parag and Prathosh, AP}, booktitle = {NeurIPS 2022 Workshop on Distribution Shifts: Connecting Methods and Applications}, year = {2022}, url = {https://openreview.net/pdf?id=yWf4wxAUcDo}, } - IEEE TSP
 FadeLoc: Smart Device Localization for Generalized κ- μ Faded IoT EnvironmentAnkur Pandey*, Piyush Tiwary*, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022
FadeLoc: Smart Device Localization for Generalized κ- μ Faded IoT EnvironmentAnkur Pandey*, Piyush Tiwary*, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2022In this paper, we propose FadeLoc a novel method for localizing smart devices in an Internet of Things (IoT) environment, based on the Received Signal Strength (RSS), and a generic κ- μ fading model where κand μdenote the fading parameters. The RSS-based localization is challenging because of noise, fading, and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) effects, thus necessitating an appropriate fading model to best fit the varying RSS values. The advantage of a generic fading model is that it can accommodate all existing fading distributions based on the estimate of κand μ. Hence, the localization can be performed for any fading environment. We derive the maximum likelihood estimate of the smart device location using a generic κ- μ fading model considering the Large and Small approximations of modified first-order Bessel function and propose an adaptive order selection method with high localization accuracy and faster convergence. We also analyze the convergence of the gradient ascent method for the κ- μ fading model. The proposed method is evaluated on a simulated κ- μ fading environment, real outdoor environment, and a complex indoor fading environment. The average localization errors are 2.07 m, 3.5 m, and 0.5 m, respectively, for the three experimental settings, outperforming the state-of-the-art localization methods in the presence of fading.
@article{9797867, author = {Pandey, Ankur and Tiwary, Piyush and Kumar, Sudhir and Das, Sajal K.}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing}, title = {FadeLoc: Smart Device Localization for Generalized ${\kappa {-} \mu}$ Faded IoT Environment}, year = {2022}, volume = {70}, pages = {3206-3220}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/TSP.2022.3183527}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9797867}, issn = {1941-0476}, } - MIT QSSTowards establishing a research lineage via identification of significant citationsTirthankar Ghosal*, Piyush Tiwary*, Robert Patton, and 1 more authorQuantitative Science Studies, Feb 2022
Finding the lineage of a research topic is crucial for understanding the prior state of the art and advancing scientific displacement. The deluge of scholarly articles makes it difficult to locate the most relevant previous work. It causes researchers to spend a considerable amount of time building up their literature list. Citations play a crucial role in discovering relevant literature. However, not all citations are created equal. The majority of the citations that a paper receives provide contextual and background information to the citing papers. In those cases, the cited paper is not central to the theme of citing papers. However, some papers build upon a given paper and further the research frontier. In those cases, the concerned cited paper plays a pivotal role in the citing paper. Hence, the nature of the citation that the former receives from the latter is significant. In this work, we discuss our investigations towards discovering significant citations of a given paper. We further show how we can leverage significant citations to build a research lineage via a significant citation graph. We demonstrate the efficacy of our idea with two real-life case studies. Our experiments yield promising results with respect to the current state of the art in classifying significant citations, outperforming the earlier ones by a relative margin of 20 points in terms of precision. We hypothesize that such an automated system can facilitate relevant literature discovery and help identify knowledge flow for a particular category of papers.
@article{10.1162/qss_a_00170, author = {Ghosal, Tirthankar and Tiwary, Piyush and Patton, Robert and Stahl, Christopher}, title = {{Towards establishing a research lineage via identification of significant citations}}, journal = {Quantitative Science Studies}, volume = {2}, number = {4}, pages = {1511-1528}, year = {2022}, month = feb, issn = {2641-3337}, doi = {10.1162/qss_a_00170}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1162/qss\_a\_00170}, }
2021
- IEEE SENSLNovel Differential r-Vectors for Localization in IoT NetworksPiyush Tiwary, Ankur Pandey, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIEEE Sensors Letters, Jun 2021
Wireless fidelity received signal strength (RSS) fingerprints are widely used for localization. However, device heterogeneity and temporal variation in the RSS values are the bottlenecks for accurate localization in the Internet of Things (IoT) networks. This letter addresses these challenges by proposing a novel differential r-vectors which are the device-invariant signature of a particular location and are invariant, even with temporal RSS variations. The proposed network addresses the vanishing gradient problem which occurs in existing deep learning based localization methods, and hence, the localization accuracy improves. We evaluate the proposed method on two real-world datasets comprising device heterogeneity and temporal RSS variations. Additionally, the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art fingerprinting-based methods that address these issues.
@article{9440753, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Pandey, Ankur and Kumar, Sudhir and Youssef, Moustafa}, journal = {IEEE Sensors Letters}, title = {Novel Differential $r$-Vectors for Localization in IoT Networks}, year = {2021}, volume = {5}, number = {6}, pages = {1-4}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/LSENS.2021.3083500}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9440753}, issn = {2475-1472}, month = jun, } - IEEE JIoTAdaptive Mini-Batch Gradient-Ascent-Based Localization for Indoor IoT Networks Under Rayleigh Fading ConditionsAnkur Pandey, Piyush Tiwary, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIEEE Internet of Things Journal, Jul 2021
Location estimation in an indoor Internet-of-Things (IoT) environment is a challenging task due to multipath signals and obstacles that cause shadowing and fading effects, and change the received signal power considerably. Most of the existing path-loss-based localization methods assume only a lognormal shadowing model and ignore small scale fading effects. This article considers a generic combined lognormal shadowing and Rayleigh fading model for efficient localization of smart devices in an indoor IoT environment. In particular, the maximum likelihood estimate of the location and path-loss exponent (PLE), and Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB) are derived. The localization parameters are estimated using a novel adaptive mini-batch gradient ascent method that maximizes the log-likelihood function with an appropriate batch size based on the convergence factor. Hence, the proposed method addresses the challenge of an arbitrary selection of a fixed batch size for a gradient ascent method by utilizing this convergence factor. Performance evaluation by a simulation study and real experiments from an indoor IoT testbed provide a more accurate joint estimation of model parameters and smart device localization.
@article{9310318, author = {Pandey, Ankur and Tiwary, Piyush and Kumar, Sudhir and Das, Sajal K.}, journal = {IEEE Internet of Things Journal}, title = {Adaptive Mini-Batch Gradient-Ascent-Based Localization for Indoor IoT Networks Under Rayleigh Fading Conditions}, year = {2021}, volume = {8}, number = {13}, pages = {10665-10677}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/JIOT.2020.3047982}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9310318}, issn = {2327-4662}, month = jul, } - IEEE COMSNETSDifferential d-Vectors for RSS based Localization in Dynamic IoT NetworksPiyush Tiwary, Ankur Pandey, and Sudhir KumarIn 2021 International Conference on COMmunication Systems & NETworkS (COMSNETS), Jan 2021
Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi) Received Signal Strength (RSS) fingerprints are frequently used for localization in Internet of Things (IoT) environment. However, RSS fingerprinting based localization methods’ accuracy degrades due to device heterogeneity and temporal variations (dynamic variations) in the target environment. In this paper, we propose a smart device localization method that addresses the dynamic RSS variations using differential d-vectors. The d-vector is the signature of a particular location and is persistent even with dynamic RSS variations. We compute the performance of the proposed d-vectors on two popular real-world datasets, and the obtained results outperform state-of-the-art fingerprinting methods that address the heterogeneity and temporal variations of the RSS values.
@inproceedings{9352896, author = {Tiwary, Piyush and Pandey, Ankur and Kumar, Sudhir}, booktitle = {2021 International Conference on COMmunication Systems & NETworkS (COMSNETS)}, title = {Differential d-Vectors for RSS based Localization in Dynamic IoT Networks}, year = {2021}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {82-85}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/COMSNETS51098.2021.9352896}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9352896}, issn = {2155-2509}, month = jan, } - NAACL WorkshopIITP-CUNI@3C: Supervised Approaches for Citation Classification (Task A) and Citation Significance Detection (Task B)Kamal Kaushik Varanasi, Tirthankar Ghosal, Piyush Tiwary, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Scholarly Document Processing, Jun 2021
Citations are crucial to a scientific discourse. Besides providing additional contexts to research papers, citations act as trackers of the direction of research in a field and as an important measure in understanding the impact of a research publication. With the rapid growth in research publications, automated solutions for identifying the purpose and influence of citations are becoming very important. The 3C Citation Context Classification Task organized as part of the Second Workshop on Scholarly Document Processing @ NAACL 2021 is a shared task to address the aforementioned problems. In this paper, we present our team, IITP-CUNI@3C’s submission to the 3C shared tasks. For Task A, citation context purpose classification, we propose a neural multi-task learning framework that harnesses the structural information of the research papers and the relation between the citation context and the cited paper for citation classification. For Task B, citation context influence classification, we use a set of simple features to classify citations based on their perceived significance. We achieve comparable performance with respect to the best performing systems in Task A and superseded the majority baseline in Task B with very simple features.
@inproceedings{varanasi-etal-2021-iitp, title = {IITP-CUNI@3C: Supervised Approaches for Citation Classification (Task A) and Citation Significance Detection (Task {B})}, author = {Varanasi, Kamal Kaushik and Ghosal, Tirthankar and Tiwary, Piyush and Singh, Muskaan}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Scholarly Document Processing}, month = jun, year = {2021}, address = {Online}, publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics}, url = {https://aclanthology.org/2021.sdp-1.19}, pages = {140--145}, }
2020
- IEEE ICCCNResidual Neural Networks for Heterogeneous Smart Device Localization in IoT NetworksAnkur Pandey, Piyush Tiwary, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIn 2020 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN), Aug 2020
Location-based services assume significant importance in the Internet of Things (IoT) based systems. In the scenarios where the satellite signals are not available or weak, the Global Positioning System (GPS) accuracy degrades sharply. Therefore, opportunistic signals can be utilized for smart device localization. In this paper, we propose a smart device localization method using residual neural networks. The proposed network is generic and performs smart device localization using opportunistic signals such as Wireless Fidelity (Wi-Fi), geomagnetic, temperature, pressure, humidity, and light signals in the IoT network. Additionally, the proposed method addresses the two significant challenges in IoT based smart device localization, which are noise and device heterogeneity. The experiments are performed on three real datasets of different opportunistic signals. Results show that the proposed method is robust to noise, and a significant improvement in the localization accuracy is obtained as compared to the state-of-the-art localization methods.
@inproceedings{9209703, author = {Pandey, Ankur and Tiwary, Piyush and Kumar, Sudhir and Das, Sajal K}, booktitle = {2020 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks (ICCCN)}, title = {Residual Neural Networks for Heterogeneous Smart Device Localization in IoT Networks}, year = {2020}, volume = {}, number = {}, pages = {1-9}, keywords = {}, doi = {10.1109/ICCCN49398.2020.9209703}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9209703}, issn = {2637-9430}, month = aug, }
2019
- ACM ICDCNA Hybrid Classifier Approach to Multivariate Sensor Data for Climate Smart Agriculture Cyber-Physical SystemsAnkur Pandey, Piyush Tiwary, Sudhir Kumar, and 1 more authorIn Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking, Bangalore, India, Aug 2019
In this paper, we propose a novel climate-smart Agriculture Cyber-Physical System (ACPS) for precision farming. The primary motive of the ACPS is to perform real-time fault location tracking in the agricultural field using multivariate sensor data. The computing model in the ACPS uses a novel hybrid classification approach which combines two classifiers for the location estimation of the sensor node. The novelty of the proposed method lies in predicting the locations that need more irrigation, soil nutrients or immediate human intervention using the sensor data. We also derive the computational complexity of the proposed method. The location accuracy improves reasonably as compared to the current-state-of-the-art methods.
@inproceedings{10.1145/3288599.3288621, author = {Pandey, Ankur and Tiwary, Piyush and Kumar, Sudhir and Das, Sajal K}, title = {A Hybrid Classifier Approach to Multivariate Sensor Data for Climate Smart Agriculture Cyber-Physical Systems}, year = {2019}, isbn = {9781450360944}, publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery}, address = {New York, NY, USA}, url = {https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3288599.3288621}, doi = {10.1145/3288599.3288621}, booktitle = {Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Distributed Computing and Networking}, pages = {337–341}, numpages = {5}, keywords = {smart agriculture, machine learning, location estimation, wireless sensor networks, cyber-physical systems}, location = {Bangalore, India}, series = {ICDCN '19}, }